 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
 Blogs
Blogs
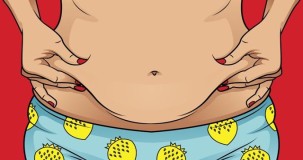 Blogs
Blogs
 Blogs
Blogs
 Baby
Baby
 Baby
Baby
 Baby
Baby
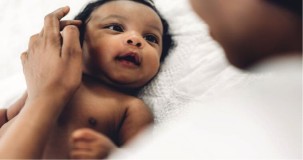 Baby
Baby
 Lifestyle
Lifestyle
What is the difference between the Lifeline and emergency broadband? Difference between Lifeline and emergency broadband. Lifeline is a federal program that provides discounted phone and internet services to low-income households, while emergency broadband is a temporary program that offers internet subsidies during emergencies, such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
As a content and marketing expert in the field, it is crucial to understand the key distinctions between the Lifeline and Emergency Broadband programs. These programs, initiated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), aim to provide affordable internet and communication services to low-income households. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of these programs and explore their unique features and benefits.
1. Lifeline:
The Lifeline program was established in 1985 and is geared towards assisting eligible low-income individuals and families by providing them access to discounted telephone services. Over the years, the program has been expanded to include broadband internet services as well. Lifeline helps bridge the digital divide by subsidizing a portion of the monthly service fees incurred by eligible beneficiaries.
Here are some key features of the Lifeline program:
1.1 Eligibility:
To qualify for Lifeline, individuals must meet certain income criteria or participate in specific assistance programs such as Medicaid, Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), Federal Public Housing Assistance (FPHA), and more. Eligibility varies by state, and the program is available to one household per qualified individual.
1.2 Benefits:
Lifeline offers a discount of up to $9.25 per month on eligible telephone or internet services. The specific discount amount may vary depending on the state and the chosen service provider. However, it is important to note that only one Lifeline discount is available per household, regardless of the number of eligible individuals.
1.3 Service Providers:
Lifeline is a national program, and numerous service providers participate in it. These providers offer various plans, including both telephone and broadband services. Individuals can choose the provider and plan that best fits their needs and budget within the framework of the Lifeline program.
2. Emergency Broadband:
The Emergency Broadband program was launched in response to the COVID-19 pandemic to further address the connectivity needs of low-income households. It aims to provide temporary financial assistance to eligible households, helping them afford broadband internet during these challenging times.
Let's explore the distinct features of the Emergency Broadband program:
2.1 Eligibility:
Eligibility for the Emergency Broadband program is quite similar to Lifeline, with participants qualifying based on their income or enrollment in specific assistance programs. Additionally, there is a provision for individuals who have experienced a substantial loss of income due to job loss or furlough since February 29, 2020.
2.2 Benefits:
The Emergency Broadband program offers a discount of up to $50 per month, or $75 per month for households on tribal lands, for broadband services. Additionally, there is an opportunity to receive a one-time discount on a device purchase. The program highlight is that it provides enhanced benefits during the ongoing pandemic until the funds are exhausted or six months after the official end of the pandemic.
2.3 Service Providers:
Similar to Lifeline, the Emergency Broadband program has numerous participating service providers across the country. These providers offer a variety of broadband plans, allowing eligible households to choose the most suitable option that aligns with their needs and preferences.
Conclusion:
While both the Lifeline and Emergency Broadband programs cater to the connectivity needs of low-income households, there are notable differences between them. Lifeline provides a standard monthly discount on eligible services, while the Emergency Broadband program offers increased benefits and temporary financial assistance during the ongoing pandemic. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for individuals seeking affordable and reliable internet access, ensuring they can make well-informed decisions and benefit from the program that best suits their requirements.
The Lifeline program is a federal assistance program in the United States that provides discounted phone and internet services to low-income households.
What is the emergency broadband program?The emergency broadband program is a temporary program established by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to help low-income households stay connected during the COVID-19 pandemic. It provides eligible households with a monthly discount on broadband services.
Who qualifies for the Lifeline program?To qualify for the Lifeline program, individuals must have an income at or below 135% of the federal poverty guidelines or participate in certain federal assistance programs, such as Medicaid, Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), or Supplemental Security Income (SSI).
Who qualifies for the emergency broadband program?Eligibility for the emergency broadband program is similar to the Lifeline program. Individuals who have experienced a substantial loss of income due to job loss or furlough since February 29, 2020, and have a total household income at or below 135% of the federal poverty guidelines can qualify.
What services are covered under the Lifeline and emergency broadband programs?The Lifeline program offers a monthly discount on either phone services or internet services. The emergency broadband program specifically provides a discount on broadband services to help households stay connected for education, work, healthcare, and other essential needs during the pandemic.
 LATEST ARTICLES
LATEST ARTICLES

Am I a Millennial or Gen Z?

Am I bloated or fat?

Am I dehydrated or sick?

Are babies born with ADHD?

Are babies born geniuses?

Are babies born in September smarter?

Are babies actually talking when they babble?

What are 3 signs of a toxic relationship?

What are 10 signs of a toxic relationship?

Am I in a toxic relationship?

How do you find red flags in a toxic relationship?

Am I bloated or pregnant?

Am I bloated or showing at 9 weeks?

Am I bloated or showing at 10 weeks?

Am I bloated or showing at 7 weeks?

Are acai bowls just smoothies?

Are all pumpkins good for soup?

Are acai bowls healthy or unhealthy?

Are air fried potatoes healthy?

Are albondigas the same as meatballs?

Am I being Gaslit or am I the gaslighter?

Am I bloated or did I gain weight?

Am I allergic to vodka?
 POPULAR ARTICLES
POPULAR ARTICLES

Am I a Millennial or Gen Z?

Am I bloated or fat?

Am I dehydrated or sick?

Are babies born with ADHD?

Are babies born geniuses?

Are babies born in September smarter?

Are babies actually talking when they babble?

What are 3 signs of a toxic relationship?

What are 10 signs of a toxic relationship?

Am I in a toxic relationship?